Is there a way to externalize mongodb connection info?
You could use environment variables. Also, you could use settings.js to set those if you wanted to (from a file for example).
Thank You for the reply,
Do I use something like global.get("mongodbUri") in the mongodb connection URI or do I need to do it a different way?
Nodes should simply accept an environment variable in the format ${varname} in a configuration input text field.
Thank You, those suggestions were very helpfull
Hi and Happy Christmas to everybody. 

I'm having difficulties in declaring my custom ENV variables following the instructions provided in this link https://flows.nodered.org/flow/8a13d11dfe80e279df83341e3e17bcc1 in order to be able to use the pre-set ENV variables in some configuration nodes (i.e. MQTT server, etc...). I'm currently running Node-Red v 0.20.7 on a Raspberry Pi.
To be clear I've made this modification to the Node-Red settings.js file:
-
add the following line
process.env.TEST = "hello world";
at the beginning of the settings.js file (before themodule.export = {.....etc..}statement). -
add the following line
env: process.envwithin the functionGlobalContext section. Now this section looks like this:
functionGlobalContext: { env:process.env },
Then I restart the Raspberry Pi (I use Node-Red on RASP Jessie OS).
But when I try to read from within a node the value of the TEST variabile - by using $(TEST) within a string field of a Change node - I always retrieve the same value $(TEST). This means that the ENV variable I defined in the settings.js config file has not been repaced by Node-Red at startup..
How is it possible? Can someone give me some advice? Is there something that I'm missing? 
Did you examine/try the flow in that writeup to see how it works?
Sorry I didn't get your question ... What do you mean with examinetry? Do you mean examine?
@lenny1972 please use backticks (`) rather than stars to highlight code. As you can see in your post, some of the code is unreadable.
Can you share exactly how you have configured the Change node?
You don't need to edit functionGlobalContext to expose process.env these days. In the function node you can use env.get("test").
typo - missing a / - I edited the post
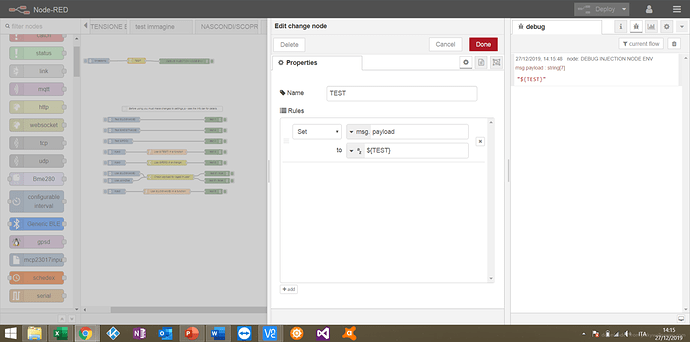
Sorry Nick for the msg formatting (I just used the bold and italic buttons in the Reply editor, I edited the post). Attached a snapshot of the Change Node configuration
I just tried this again and it works find so what is the differences??
What version of NR?
What version of node.js?
what platform are you running on?
please copy and past the section of your settings.js that shows where you added your env. It should look something like this:
// The `https` setting requires the `fs` module. Uncomment the following
// to make it available:
//var fs = require("fs");
process.env.FOO = 'just another bar';
process.env.TZ = "America/New York";
process.env.TEST = "hello world";
module.exports = {
The change node can be set to point directly at an env variable

Below the content of the first lines of my settings.js file
// The `https` setting requires the `fs` module. Uncomment the following
// to make it available:
//var fs = require("fs");
//inizio variabili ambiente mie
process.env.TEST = "leonardo";
//process.env.FOO = "hello world!";
// fine variabili ambiente mie
module.exports = {
For completeness I attach the entire settings.js file
/**
* Copyright JS Foundation and other contributors, http://js.foundation
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
**/
// The `https` setting requires the `fs` module. Uncomment the following
// to make it available:
//var fs = require("fs");
//inizio variabili ambiente mie
process.env.TEST = "leonardo";
//process.env.FOO = "hello world!";
// fine variabili ambiente mie
module.exports = {
// the tcp port that the Node-RED web server is listening on
uiPort: process.env.PORT || 1880,
// By default, the Node-RED UI accepts connections on all IPv4 interfaces.
// To listen on all IPv6 addresses, set uiHost to "::",
// The following property can be used to listen on a specific interface. For
// example, the following would only allow connections from the local machine.
//uiHost: "127.0.0.1",
// Retry time in milliseconds for MQTT connections
mqttReconnectTime: 15000,
// Retry time in milliseconds for Serial port connections
serialReconnectTime: 15000,
// Retry time in milliseconds for TCP socket connections
//socketReconnectTime: 10000,
// Timeout in milliseconds for TCP server socket connections
// defaults to no timeout
//socketTimeout: 120000,
// Maximum number of messages to wait in queue while attempting to connect to TCP socket
// defaults to 1000
//tcpMsgQueueSize: 2000,
// Timeout in milliseconds for HTTP request connections
// defaults to 120 seconds
//httpRequestTimeout: 120000,
// The maximum length, in characters, of any message sent to the debug sidebar tab
debugMaxLength: 1000,
// The maximum number of messages nodes will buffer internally as part of their
// operation. This applies across a range of nodes that operate on message sequences.
// defaults to no limit. A value of 0 also means no limit is applied.
//nodeMaxMessageBufferLength: 0,
// To disable the option for using local files for storing keys and certificates in the TLS configuration
// node, set this to true
//tlsConfigDisableLocalFiles: true,
// Colourise the console output of the debug node
//debugUseColors: true,
// The file containing the flows. If not set, it defaults to flows_<hostname>.json
//flowFile: 'flows.json',
// To enabled pretty-printing of the flow within the flow file, set the following
// property to true:
//flowFilePretty: true,
// By default, credentials are encrypted in storage using a generated key. To
// specify your own secret, set the following property.
// If you want to disable encryption of credentials, set this property to false.
// Note: once you set this property, do not change it - doing so will prevent
// node-red from being able to decrypt your existing credentials and they will be
// lost.
//credentialSecret: "a-secret-key",
// By default, all user data is stored in the Node-RED install directory. To
// use a different location, the following property can be used
//userDir: '/home/nol/.node-red/',
// Node-RED scans the `nodes` directory in the install directory to find nodes.
// The following property can be used to specify an additional directory to scan.
//nodesDir: '/home/nol/.node-red/nodes',
// By default, the Node-RED UI is available at http://localhost:1880/
// The following property can be used to specify a different root path.
// If set to false, this is disabled.
//httpAdminRoot: '/admin',
// Some nodes, such as HTTP In, can be used to listen for incoming http requests.
// By default, these are served relative to '/'. The following property
// can be used to specifiy a different root path. If set to false, this is
// disabled.
//httpNodeRoot: '/red-nodes',
// The following property can be used in place of 'httpAdminRoot' and 'httpNodeRoot',
// to apply the same root to both parts.
//httpRoot: '/red',
// When httpAdminRoot is used to move the UI to a different root path, the
// following property can be used to identify a directory of static content
// that should be served at http://localhost:1880/.
httpStatic: '/home/pi/Immagini_APA',
// The maximum size of HTTP request that will be accepted by the runtime api.
// Default: 5mb
//apiMaxLength: '5mb',
// If you installed the optional node-red-dashboard you can set it's path
// relative to httpRoot
//ui: { path: "ui" },
// Securing Node-RED
// -----------------
// To password protect the Node-RED editor and admin API, the following
// property can be used. See http://nodered.org/docs/security.html for details.
adminAuth: {
type: "credentials",
users: [{
username: "admin",
password: "myPassword",
permissions: "*"
}],
sessionExpiryTime:86400
},
// To password protect the node-defined HTTP endpoints (httpNodeRoot), or
// the static content (httpStatic), the following properties can be used.
// The pass field is a bcrypt hash of the password.
// See http://nodered.org/docs/security.html#generating-the-password-hash
httpNodeAuth: {user:"user",pass:"user_password"},
// The following property can be used to enable HTTPS
// See http://nodejs.org/api/https.html#https_https_createserver_options_requestlistener
// for details on its contents.
// See the comment at the top of this file on how to load the `fs` module used by
// this setting.
//
//https: {
// key: fs.readFileSync('/node-key.pem'),
// cert: fs.readFileSync('/node-cert.pem')
//},
// The following property can be used to cause insecure HTTP connections to
// be redirected to HTTPS.
//requireHttps: true
// The following property can be used to disable the editor. The admin API
// is not affected by this option. To disable both the editor and the admin
// API, use either the httpRoot or httpAdminRoot properties
//disableEditor: false,
// The following property can be used to configure cross-origin resource sharing
// in the HTTP nodes.
// See https://github.com/troygoode/node-cors#configuration-options for
// details on its contents. The following is a basic permissive set of options:
//httpNodeCors: {
// origin: "*",
// methods: "GET,PUT,POST,DELETE"
//},
// If you need to set an http proxy please set an environment variable
// called http_proxy (or HTTP_PROXY) outside of Node-RED in the operating system.
// For example - http_proxy=http://myproxy.com:8080
// (Setting it here will have no effect)
// You may also specify no_proxy (or NO_PROXY) to supply a comma separated
// list of domains to not proxy, eg - no_proxy=.acme.co,.acme.co.uk
// The following property can be used to add a custom middleware function
// in front of all http in nodes. This allows custom authentication to be
// applied to all http in nodes, or any other sort of common request processing.
//httpNodeMiddleware: function(req,res,next) {
// // Handle/reject the request, or pass it on to the http in node by calling next();
// // Optionally skip our rawBodyParser by setting this to true;
// //req.skipRawBodyParser = true;
// next();
//},
// The following property can be used to verify websocket connection attempts.
// This allows, for example, the HTTP request headers to be checked to ensure
// they include valid authentication information.
//webSocketNodeVerifyClient: function(info) {
// // 'info' has three properties:
// // - origin : the value in the Origin header
// // - req : the HTTP request
// // - secure : true if req.connection.authorized or req.connection.encrypted is set
// //
// // The function should return true if the connection should be accepted, false otherwise.
// //
// // Alternatively, if this function is defined to accept a second argument, callback,
// // it can be used to verify the client asynchronously.
// // The callback takes three arguments:
// // - result : boolean, whether to accept the connection or not
// // - code : if result is false, the HTTP error status to return
// // - reason: if result is false, the HTTP reason string to return
//},
// Anything in this hash is globally available to all functions.
// It is accessed as context.global.
// eg:
// functionGlobalContext: { os:require('os') }
// can be accessed in a function block as:
// context.global.os
functionGlobalContext: {
// os:require('os'),
// jfive:require("johnny-five"),
// j5board:require("johnny-five").Board({repl:false})
},
// Context Storage
// The following property can be used to enable context storage. The configuration
// provided here will enable file-based context that flushes to disk every 30 seconds.
// Refer to the documentation for further options: https://nodered.org/docs/api/context/
//
//contextStorage: {
// default: {
// module:"localfilesystem"
// },
//},
// The following property can be used to order the categories in the editor
// palette. If a node's category is not in the list, the category will get
// added to the end of the palette.
// If not set, the following default order is used:
//paletteCategories: ['subflows', 'input', 'output', 'function', 'social', 'mobile', 'storage', 'analysis', 'advanced'],
// Configure the logging output
logging: {
// Only console logging is currently supported
console: {
// Level of logging to be recorded. Options are:
// fatal - only those errors which make the application unusable should be recorded
// error - record errors which are deemed fatal for a particular request + fatal errors
// warn - record problems which are non fatal + errors + fatal errors
// info - record information about the general running of the application + warn + error + fatal errors
// debug - record information which is more verbose than info + info + warn + error + fatal errors
// trace - record very detailed logging + debug + info + warn + error + fatal errors
// off - turn off all logging (doesn't affect metrics or audit)
level: "debug",
// Whether or not to include metric events in the log output
metrics: false,
// Whether or not to include audit events in the log output
audit: false
}
},
// Customising the editor
editorTheme: {
projects: {
// To enable the Projects feature, set this value to true
enabled: false
}
},
}
Any ideas why it doesn't work?
Thanks Dceejay I know it. I was just making some test with a Change node before configuring the ENV within the MQTT configuration/input/output nodes. MQTT node didn't accept the "$" type but only string type.
Have you read the docs on using env vars?
https://nodered.org/docs/user-guide/environment-variables
The proper syntax for setting a node property is ${TEST}.
Odd, any node you can use eithor $(TEST) or ${TEST} and both work
Yes, but the $() is deprecated and no longer documented so I encourage people to follow what the docs says.
I fix the sintax on the Change node but with no luck...I always retrieve the value ${TEST}.... 
Any thoughts???
outside of Node-RED (but in the command windows where you start Node-RED)
try
export TEST=HelloWorld
then restart Node-RED from that same window : node-red
That should set the env variable for the whole session.