I have a problem to understand or to use external modules with new features in the function node.
I tried it first the node-json-db library and then later with the mongodb - npm library.
At least for mongodb I saw that there are nodes available.
However I want to understand why I cannot user external libraries in my function nodes. I always get errors , if I want to create an external object - that it is no constructor.
In general it seems that the definition in the function nodes are correct - as the modules are automatically installed in the users node_modules directory.

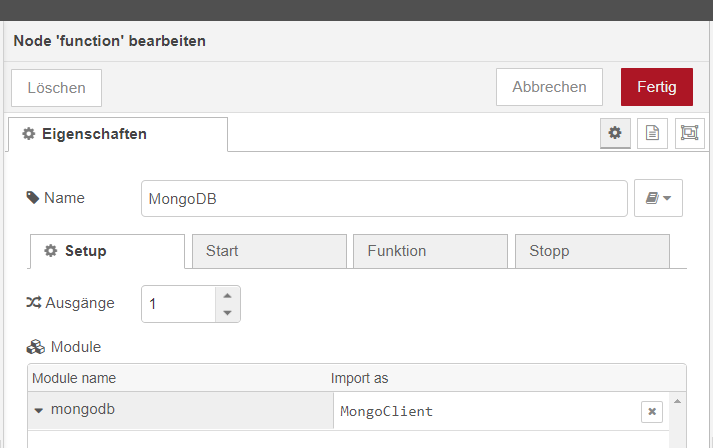
I defined the external module in the setup tab of the function node:
I always get the error that it is not a constructor to create the object of an external lib .
This happens with more than one lib.
I tried everything and checked settings.js - and as you can see the module itself has been installed.
So here is my settings.js - I recreated it with the new command node-red admin init.
So even if nodes may be already available - it would be nice to understand what is wrong, as I want to use perhaps a nodejs lib in case there is no node available.
I appreciate any help. Here is my settings.js - if this will help to analyse the error:
Zusammenfassung
/**
* Node-RED Settings created at Sun, 30 Jan 2022 01:27:56 GMT
*
* It can contain any valid JavaScript code that will get run when Node-RED
* is started.
*
* Lines that start with // are commented out.
* Each entry should be separated from the entries above and below by a comma ','
*
* For more information about individual settings, refer to the documentation:
* https://nodered.org/docs/user-guide/runtime/configuration
*
* The settings are split into the following sections:
* - Flow File and User Directory Settings
* - Security
* - Server Settings
* - Runtime Settings
* - Editor Settings
* - Node Settings
*
**/
module.exports = {
/*******************************************************************************
* Flow File and User Directory Settings
* - flowFile
* - credentialSecret
* - flowFilePretty
* - userDir
* - nodesDir
******************************************************************************/
/** The file containing the flows. If not set, defaults to flows_<hostname>.json **/
flowFile: "flows.json",
/** By default, credentials are encrypted in storage using a generated key. To
* specify your own secret, set the following property.
* If you want to disable encryption of credentials, set this property to false.
* Note: once you set this property, do not change it - doing so will prevent
* node-red from being able to decrypt your existing credentials and they will be
* lost.
*/
//credentialSecret: "a-secret-key",
/** By default, the flow JSON will be formatted over multiple lines making
* it easier to compare changes when using version control.
* To disable pretty-printing of the JSON set the following property to false.
*/
flowFilePretty: true,
/** By default, all user data is stored in a directory called `.node-red` under
* the user's home directory. To use a different location, the following
* property can be used
*/
//userDir: '/home/nol/.node-red/',
/** Node-RED scans the `nodes` directory in the userDir to find local node files.
* The following property can be used to specify an additional directory to scan.
*/
//nodesDir: '/home/nol/.node-red/nodes',
/*******************************************************************************
* Security
* - adminAuth
* - https
* - httpsRefreshInterval
* - requireHttps
* - httpNodeAuth
* - httpStaticAuth
******************************************************************************/
/** To password protect the Node-RED editor and admin API, the following
* property can be used. See http://nodered.org/docs/security.html for details.
*/
//adminAuth: {
// type: "credentials",
// users: [{
// username: "admin",
// password: "$2a$08$zZWtXTja0fB1pzD4sHCMyOCMYz2Z6dNbM6tl8sJogENOMcxWV9DN.",
// permissions: "*"
// }]
//},
/** The following property can be used to enable HTTPS
* This property can be either an object, containing both a (private) key
* and a (public) certificate, or a function that returns such an object.
* See http://nodejs.org/api/https.html#https_https_createserver_options_requestlistener
* for details of its contents.
*/
/** Option 1: static object */
//https: {
// key: require("fs").readFileSync('privkey.pem'),
// cert: require("fs").readFileSync('cert.pem')
//},
/** Option 2: function that returns the HTTP configuration object */
// https: function() {
// // This function should return the options object, or a Promise
// // that resolves to the options object
// return {
// key: require("fs").readFileSync('privkey.pem'),
// cert: require("fs").readFileSync('cert.pem')
// }
// },
/** If the `https` setting is a function, the following setting can be used
* to set how often, in hours, the function will be called. That can be used
* to refresh any certificates.
*/
//httpsRefreshInterval : 12,
/** The following property can be used to cause insecure HTTP connections to
* be redirected to HTTPS.
*/
//requireHttps: true,
/** To password protect the node-defined HTTP endpoints (httpNodeRoot),
* including node-red-dashboard, or the static content (httpStatic), the
* following properties can be used.
* The `pass` field is a bcrypt hash of the password.
* See http://nodered.org/docs/security.html#generating-the-password-hash
*/
//httpNodeAuth: {user:"user",pass:"$2a$08$zZWtXTja0fB1pzD4sHCMyOCMYz2Z6dNbM6tl8sJogENOMcxWV9DN."},
//httpStaticAuth: {user:"user",pass:"$2a$08$zZWtXTja0fB1pzD4sHCMyOCMYz2Z6dNbM6tl8sJogENOMcxWV9DN."},
/*******************************************************************************
* Server Settings
* - uiPort
* - uiHost
* - apiMaxLength
* - httpServerOptions
* - httpAdminRoot
* - httpAdminMiddleware
* - httpNodeRoot
* - httpNodeCors
* - httpNodeMiddleware
* - httpStatic
******************************************************************************/
/** the tcp port that the Node-RED web server is listening on */
uiPort: process.env.PORT || 1880,
/** By default, the Node-RED UI accepts connections on all IPv4 interfaces.
* To listen on all IPv6 addresses, set uiHost to "::",
* The following property can be used to listen on a specific interface. For
* example, the following would only allow connections from the local machine.
*/
//uiHost: "127.0.0.1",
/** The maximum size of HTTP request that will be accepted by the runtime api.
* Default: 5mb
*/
//apiMaxLength: '5mb',
/** The following property can be used to pass custom options to the Express.js
* server used by Node-RED. For a full list of available options, refer
* to http://expressjs.com/en/api.html#app.settings.table
*/
//httpServerOptions: { },
/** By default, the Node-RED UI is available at http://localhost:1880/
* The following property can be used to specify a different root path.
* If set to false, this is disabled.
*/
//httpAdminRoot: '/admin',
/** The following property can be used to add a custom middleware function
* in front of all admin http routes. For example, to set custom http
* headers. It can be a single function or an array of middleware functions.
*/
// httpAdminMiddleware: function(req,res,next) {
// // Set the X-Frame-Options header to limit where the editor
// // can be embedded
// //res.set('X-Frame-Options', 'sameorigin');
// next();
// },
/** Some nodes, such as HTTP In, can be used to listen for incoming http requests.
* By default, these are served relative to '/'. The following property
* can be used to specifiy a different root path. If set to false, this is
* disabled.
*/
//httpNodeRoot: '/red-nodes',
/** The following property can be used to configure cross-origin resource sharing
* in the HTTP nodes.
* See https://github.com/troygoode/node-cors#configuration-options for
* details on its contents. The following is a basic permissive set of options:
*/
//httpNodeCors: {
// origin: "*",
// methods: "GET,PUT,POST,DELETE"
//},
/** If you need to set an http proxy please set an environment variable
* called http_proxy (or HTTP_PROXY) outside of Node-RED in the operating system.
* For example - http_proxy=http://myproxy.com:8080
* (Setting it here will have no effect)
* You may also specify no_proxy (or NO_PROXY) to supply a comma separated
* list of domains to not proxy, eg - no_proxy=.acme.co,.acme.co.uk
*/
/** The following property can be used to add a custom middleware function
* in front of all http in nodes. This allows custom authentication to be
* applied to all http in nodes, or any other sort of common request processing.
* It can be a single function or an array of middleware functions.
*/
//httpNodeMiddleware: function(req,res,next) {
// // Handle/reject the request, or pass it on to the http in node by calling next();
// // Optionally skip our rawBodyParser by setting this to true;
// //req.skipRawBodyParser = true;
// next();
//},
/** When httpAdminRoot is used to move the UI to a different root path, the
* following property can be used to identify a directory of static content
* that should be served at http://localhost:1880/.
*/
//httpStatic: '/home/nol/node-red-static/',
/*******************************************************************************
* Runtime Settings
* - lang
* - logging
* - contextStorage
* - exportGlobalContextKeys
* - externalModules
******************************************************************************/
/** Uncomment the following to run node-red in your preferred language.
* Available languages include: en-US (default), ja, de, zh-CN, zh-TW, ru, ko
* Some languages are more complete than others.
*/
// lang: "de",
/** Configure the logging output */
logging: {
/** Only console logging is currently supported */
console: {
/** Level of logging to be recorded. Options are:
* fatal - only those errors which make the application unusable should be recorded
* error - record errors which are deemed fatal for a particular request + fatal errors
* warn - record problems which are non fatal + errors + fatal errors
* info - record information about the general running of the application + warn + error + fatal errors
* debug - record information which is more verbose than info + info + warn + error + fatal errors
* trace - record very detailed logging + debug + info + warn + error + fatal errors
* off - turn off all logging (doesn't affect metrics or audit)
*/
level: "info",
/** Whether or not to include metric events in the log output */
metrics: false,
/** Whether or not to include audit events in the log output */
audit: false
}
},
/** Context Storage
* The following property can be used to enable context storage. The configuration
* provided here will enable file-based context that flushes to disk every 30 seconds.
* Refer to the documentation for further options: https://nodered.org/docs/api/context/
*/
//contextStorage: {
// default: {
// module:"localfilesystem"
// },
//},
/** `global.keys()` returns a list of all properties set in global context.
* This allows them to be displayed in the Context Sidebar within the editor.
* In some circumstances it is not desirable to expose them to the editor. The
* following property can be used to hide any property set in `functionGlobalContext`
* from being list by `global.keys()`.
* By default, the property is set to false to avoid accidental exposure of
* their values. Setting this to true will cause the keys to be listed.
*/
exportGlobalContextKeys: false,
/** Configure how the runtime will handle external npm modules.
* This covers:
* - whether the editor will allow new node modules to be installed
* - whether nodes, such as the Function node are allowed to have their
* own dynamically configured dependencies.
* The allow/denyList options can be used to limit what modules the runtime
* will install/load. It can use '*' as a wildcard that matches anything.
*/
externalModules: {
// autoInstall: false, /** Whether the runtime will attempt to automatically install missing modules */
// autoInstallRetry: 30, /** Interval, in seconds, between reinstall attempts */
// palette: { /** Configuration for the Palette Manager */
// allowInstall: true, /** Enable the Palette Manager in the editor */
// allowUpload: true, /** Allow module tgz files to be uploaded and installed */
// allowList: [],
// denyList: []
// },
// modules: { /** Configuration for node-specified modules */
// allowInstall: true,
// allowList: [],
// denyList: []
// }
},
/*******************************************************************************
* Editor Settings
* - disableEditor
* - editorTheme
******************************************************************************/
/** The following property can be used to disable the editor. The admin API
* is not affected by this option. To disable both the editor and the admin
* API, use either the httpRoot or httpAdminRoot properties
*/
//disableEditor: false,
/** Customising the editor
* See https://nodered.org/docs/user-guide/runtime/configuration#editor-themes
* for all available options.
*/
editorTheme: {
/** The following property can be used to set a custom theme for the editor.
* See https://github.com/node-red-contrib-themes/theme-collection for
* a collection of themes to chose from.
*/
//theme: "",
palette: {
/** The following property can be used to order the categories in the editor
* palette. If a node's category is not in the list, the category will get
* added to the end of the palette.
* If not set, the following default order is used:
*/
//categories: ['subflows', 'common', 'function', 'network', 'sequence', 'parser', 'storage'],
},
projects: {
/** To enable the Projects feature, set this value to true */
enabled: false,
workflow: {
/** Set the default projects workflow mode.
* - manual - you must manually commit changes
* - auto - changes are automatically committed
* This can be overridden per-user from the 'Git config'
* section of 'User Settings' within the editor
*/
mode: "manual"
}
},
codeEditor: {
/** Select the text editor component used by the editor.
* Defaults to "ace", but can be set to "ace" or "monaco"
*/
lib: "monaco",
options: {
/** The follow options only apply if the editor is set to "monaco"
*
* theme - must match the file name of a theme in
* packages/node_modules/@node-red/editor-client/src/vendor/monaco/dist/theme
* e.g. "tomorrow-night", "upstream-sunburst", "github", "my-theme"
*/
theme: "vs",
/** other overrides can be set e.g. fontSize, fontFamily, fontLigatures etc.
* for the full list, see https://microsoft.github.io/monaco-editor/api/interfaces/monaco.editor.istandaloneeditorconstructionoptions.html
*/
//fontSize: 14,
//fontFamily: "Cascadia Code, Fira Code, Consolas, 'Courier New', monospace",
//fontLigatures: true,
}
}
},
/*******************************************************************************
* Node Settings
* - fileWorkingDirectory
* - functionGlobalContext
* - functionExternalModules
* - nodeMessageBufferMaxLength
* - ui (for use with Node-RED Dashboard)
* - debugUseColors
* - debugMaxLength
* - execMaxBufferSize
* - httpRequestTimeout
* - mqttReconnectTime
* - serialReconnectTime
* - socketReconnectTime
* - socketTimeout
* - tcpMsgQueueSize
* - inboundWebSocketTimeout
* - tlsConfigDisableLocalFiles
* - webSocketNodeVerifyClient
******************************************************************************/
/** The working directory to handle relative file paths from within the File nodes
* defaults to the working directory of the Node-RED process.
*/
//fileWorkingDirectory: "",
/** Allow the Function node to load additional npm modules directly */
functionExternalModules: true,
/** The following property can be used to set predefined values in Global Context.
* This allows extra node modules to be made available with in Function node.
* For example, the following:
* functionGlobalContext: { os:require('os') }
* will allow the `os` module to be accessed in a Function node using:
* global.get("os")
*/
functionGlobalContext: {
// os:require('os'),
},
/** The maximum number of messages nodes will buffer internally as part of their
* operation. This applies across a range of nodes that operate on message sequences.
* defaults to no limit. A value of 0 also means no limit is applied.
*/
//nodeMessageBufferMaxLength: 0,
/** If you installed the optional node-red-dashboard you can set it's path
* relative to httpNodeRoot
* Other optional properties include
* readOnly:{boolean},
* middleware:{function or array}, (req,res,next) - http middleware
* ioMiddleware:{function or array}, (socket,next) - socket.io middleware
*/
//ui: { path: "ui" },
/** Colourise the console output of the debug node */
//debugUseColors: true,
/** The maximum length, in characters, of any message sent to the debug sidebar tab */
debugMaxLength: 1000,
/** Maximum buffer size for the exec node. Defaults to 10Mb */
//execMaxBufferSize: 10000000,
/** Timeout in milliseconds for HTTP request connections. Defaults to 120s */
//httpRequestTimeout: 120000,
/** Retry time in milliseconds for MQTT connections */
mqttReconnectTime: 15000,
/** Retry time in milliseconds for Serial port connections */
serialReconnectTime: 15000,
/** Retry time in milliseconds for TCP socket connections */
//socketReconnectTime: 10000,
/** Timeout in milliseconds for TCP server socket connections. Defaults to no timeout */
//socketTimeout: 120000,
/** Maximum number of messages to wait in queue while attempting to connect to TCP socket
* defaults to 1000
*/
//tcpMsgQueueSize: 2000,
/** Timeout in milliseconds for inbound WebSocket connections that do not
* match any configured node. Defaults to 5000
*/
//inboundWebSocketTimeout: 5000,
/** To disable the option for using local files for storing keys and
* certificates in the TLS configuration node, set this to true.
*/
//tlsConfigDisableLocalFiles: true,
/** The following property can be used to verify websocket connection attempts.
* This allows, for example, the HTTP request headers to be checked to ensure
* they include valid authentication information.
*/
//webSocketNodeVerifyClient: function(info) {
// /** 'info' has three properties:
// * - origin : the value in the Origin header
// * - req : the HTTP request
// * - secure : true if req.connection.authorized or req.connection.encrypted is set
// *
// * The function should return true if the connection should be accepted, false otherwise.
// *
// * Alternatively, if this function is defined to accept a second argument, callback,
// * it can be used to verify the client asynchronously.
// * The callback takes three arguments:
// * - result : boolean, whether to accept the connection or not
// * - code : if result is false, the HTTP error status to return
// * - reason: if result is false, the HTTP reason string to return
// */
//},
}
Enabling options in the externalModules object will not solve the problem. I hope someone can help me to understand the problem.

 But I am happy that it works in general. Many thanks!
But I am happy that it works in general. Many thanks!

